三角関数のサインとコサインは連続する滑らかなモーションに利用できます。
目次
サインとコサインと円
サイン(sin)とコサイン(cos)は、角度θに対する半径1の円周上の点が座標(cosθ, sinθ)にあることを言います。したがって点Pが(cosθ, sinθ)にあるとき、cosθはX軸上の0からcosθまでの長さに、sinθはY軸上の0からsinθまでの長さに当たります。
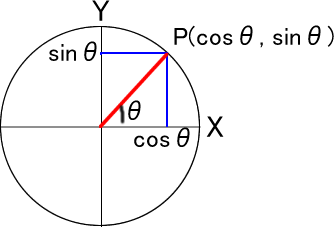
この円は半径が1なので、もっと大きくしたい場合はその半径を掛けます。また円の中心は原点(0, 0)なので、中心を移動したい場合には、それを足します。
// (centerX, centerY)を中心とする半径がradiusの円
// 円周上のx座標値
const x = centerX + cosValue * radius;
// 円周上のy座標値
const y = centerY + sinValue * radius;この計算により、角度θのときの(x, y)が分かるので、draw()関数内でθを増減させ、位置(cosθ, sinθ)にシェイプを描くと、円運動になります。
let angle = 0;
let centerX;
let centerY;
// 大きな円の半径
const radius = 80;
const speed = 0.01;
function setup() {
createCanvas(200, 200);
// キャンバスのセンターをメモ
centerX = width / 2;
centerY = height / 2;
}
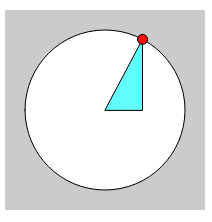
function draw() {
// angleのサイン値とコサイン値
const sinValue = sin(angle);
const cosValue = cos(angle);
background(204);
fill(255);
ellipse(centerX, centerY, 160, 160);
// 円周上のx座標値
const x = centerX + cosValue * radius;
// 円周上のy座標値
const y = centerY + sinValue * radius;
fill(100, 255, 255);
triangle(centerX, centerY, x, y, x, centerY)
fill(255, 0, 0);
// 円周上を移動する赤い円を描画
ellipse(x, y, 10, 10);
// 角度を少しずつ大きくする
angle += speed;
}
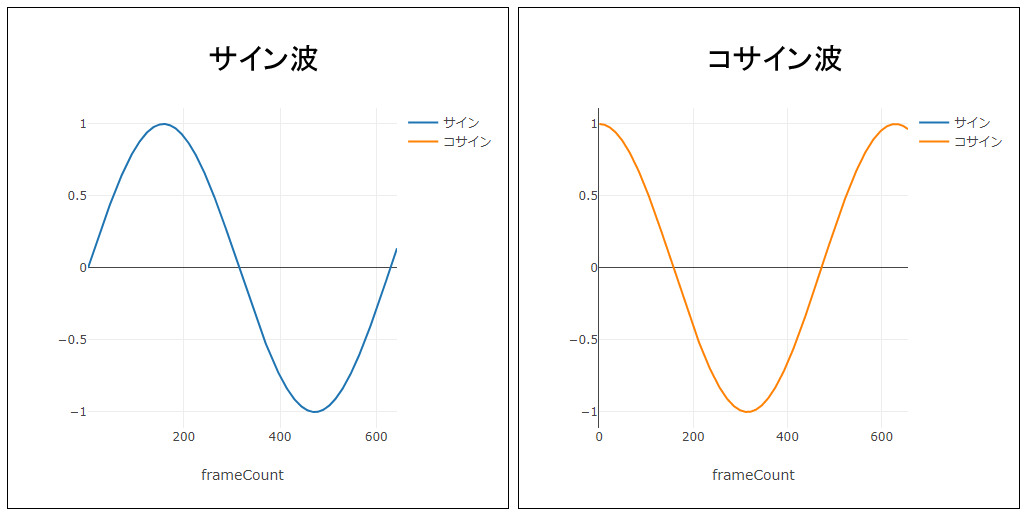
サイン波とコサイン波
p5.jsのsin()とcos()関数が返す値を、次のコードでグラフにプロットすると、サイン波とコサイン波が描画できます(plotly.jsを使用)。
let angle = 0;
const speed = 0.01;
function draw() {
// angleのサイン値とコサイン値
const sinValue = sin(angle);
const cosValue = cos(angle);
plot(frameCount, sinValue);
plot(frameCount, cosValue);
angle += speed;
}サイン波もコサイン波も、波のてっぺんと底近くで変化の度合いが緩くなり、その後向きを変えます。この曲がり具合が面白いモーションを生み出す元です。サイン波は0から始まるので、0から始めたいモーションに適していると言えます。
サイン波の動き
次の例は、sin(angle)が返すサイン値を動きに変換するうまい方法を示しています。
let angle = 0.0;
const offset = 60;
const scalar = 40;
const speed = 0.05;
function setup() {
createCanvas(240, 120);
strokeWeight(2);
stroke(255);
}
function draw() {
background(0);
const y1 = offset + sin(angle) * scalar;
const y2 = offset + sin(angle + 0.4) * scalar;
const y3 = offset + sin(angle + 0.8) * scalar;
fill(255, 0, 0);
ellipse(80, y1, 40, 40);
fill(0, 255, 0);
ellipse(120, y2, 40, 40);
fill(0, 0, 255);
ellipse(160, y3, 40, 40);
angle += speed;
}
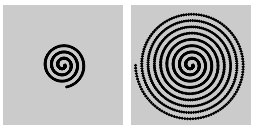
うずまき
円の半径に当たるscalar値をフレームごとに大きくすると、うずまきになります。
let angle = 0.0;
const offset = 60;
let scalar = 2;
const speed = 0.05;
function setup() {
createCanvas(120, 120);
fill(0);
background(204);
}
function draw() {
const x = offset + cos(angle) * scalar;
const y = offset + sin(angle) * scalar;
ellipse(x, y, 2, 2);
angle += speed;
scalar += speed;
}